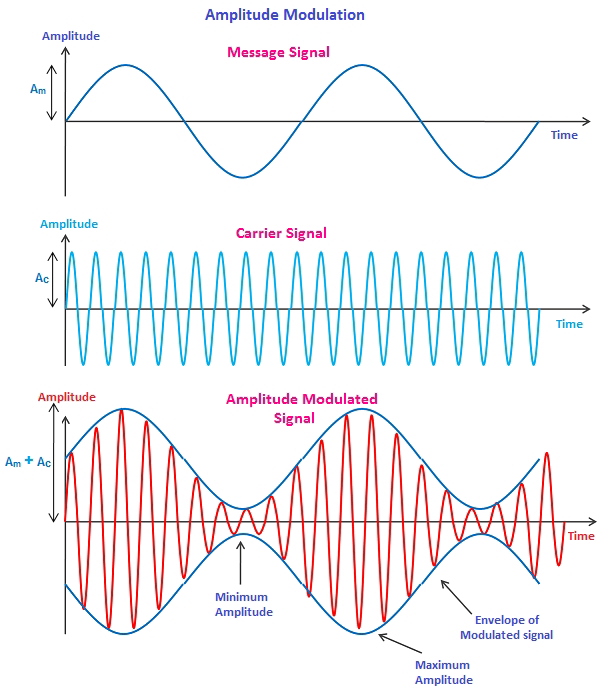
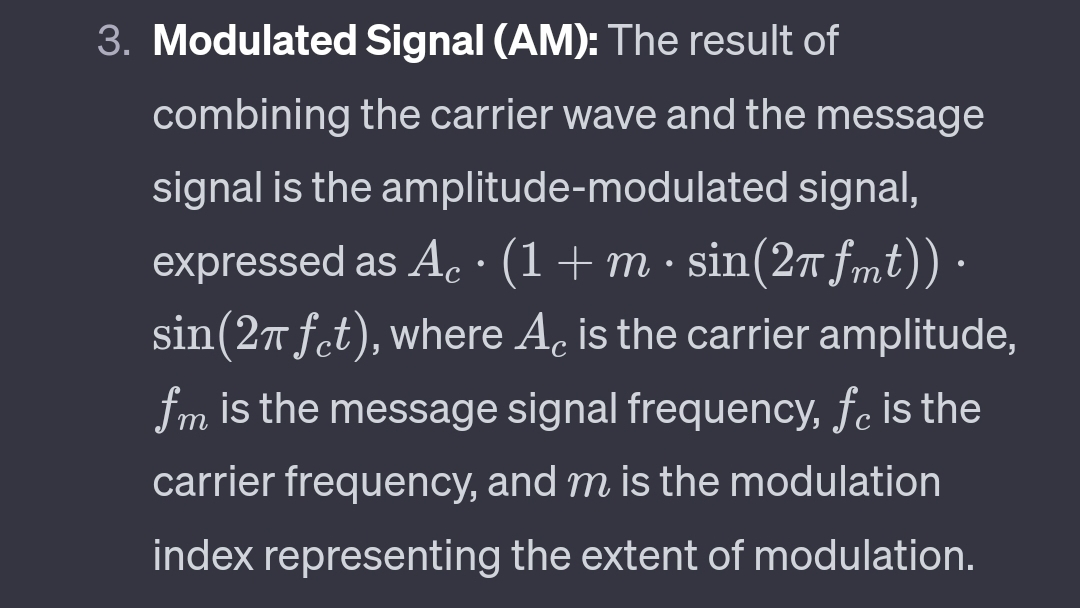
Principle of Amplitude Modulation (AM): Amplitude Modulation is a technique used in analog communication where the amplitude of a carrier wave is varied in proportion to the instantaneous amplitude of the message signal being transmitted. The carrier wave is a high-frequency signal, and the message signal is a lower-frequency signal.
Carrier Wave (C): This is a high-frequency sine wave that carries no information but provides the necessary frequency for transmission.
Message Signal (M): This is the signal containing the information to be transmitted. The amplitude variations of the message signal modulate the amplitude of the carrier wave.
Applications:
Broadcasting: AM is widely used in radio broadcasting for transmitting audio signals over long distances.
Two-Way Radio Communication: AM is used in certain two-way radio communication systems.
Navigation Systems: It has been historically used in radio navigation systems.
Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK): AM is a basis for amplitude shift keying, a digital modulation technique used in data transmission.
Remote Control Systems: AM is used in certain remote control applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages: Simple to implement, suitable for voice communication, and compatible with existing receivers.
Disadvantages: Susceptible to interference, less bandwidth-efficient compared to other modulation techniques, and not as secure as digital modulation methods.
> Understanding the principles and characteristics of AM is essential for designing and working with analog communication systems.


No comments:
Post a Comment