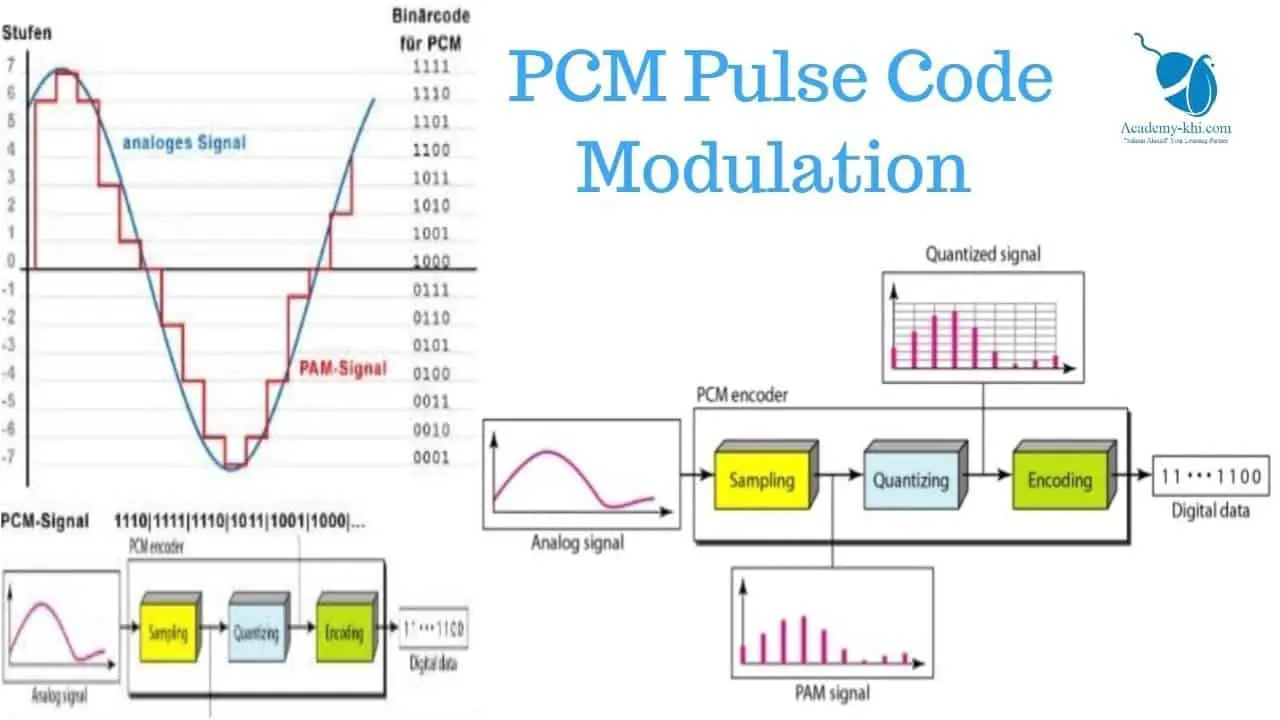
Principle of Pulse Code Modulation (PCM): Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) is a digital modulation technique used to convert analog signals into digital form for transmission or storage. PCM involves three main processes: sampling, quantization, and coding.
1. Sampling:
Definition: Sampling involves taking discrete samples of the continuous analog signal at regular intervals.
2. Quantization:
Definition: Quantization involves mapping each sample's amplitude to the nearest discrete level.
Quantization Levels (L): The number of discrete levels determines the resolution of the quantization. More levels provide higher fidelity but require more bits for representation.
Quantization Error (Noise): The difference between the actual analog sample and its quantized representation introduces quantization noise.
3. Coding:
Definition: The quantized samples are then encoded into digital words using binary code.
Bit Depth (N): The number of bits used to represent each sample. Higher bit depth allows for more precise representation but requires more data.
PCM Signal Representation: The PCM signal is a sequence of binary numbers, each representing a quantized sample.
Analysis of PCM:
Sampling Theorem: It ensures that the reconstructed signal at the receiver accurately represents the original analog signal if the sampling rate is sufficient.
Quantization Error: As the number of quantization levels increases, quantization error decreases, leading to better signal fidelity.
- Bit Rate (R): The bit rate of PCM is given byR=Fs⋅N, where the sampling rate and N is the bit depth.
Applications of PCM:
Telecommunication: PCM is widely used in voice communication, particularly in digital telephone systems.
Audio Recording: It is used in digital audio recording systems, such as CDs and digital audio broadcasting.
Medical Imaging: PCM is employed in medical imaging devices, converting analog signals from sensors into digital form for analysis.
Data Transmission: PCM is used in various digital communication systems for transmitting and receiving data.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages: Robust against noise, easy to implement in digital systems, and allows for efficient error detection and correction.
Disadvantages: Requires higher bandwidth compared to analog signals, especially for high-quality audio, due to the discrete nature of the signal.
PCM is a fundamental technique in digital communication and data storage, ensuring accurate representation and transmission of analog signals in a digital format.


No comments:
Post a Comment