Principle of Angle Modulation: Angle Modulation is a type of modulation where the angle (phase or frequency) of the carrier wave is varied in accordance with the instantaneous amplitude of the message signal. There are two main types: Phase Modulation (PM) and Frequency Modulation (FM).
1. Phase Modulation (PM): In PM, the instantaneous phase of the carrier wave is varied in proportion to the amplitude of the message signal. The mathematical representation of a phase-modulated signal is:
Analysis of PM:
Phase Deviation (Δφ): It represents the maximum phase change in radians and is proportional to the peak amplitude of the message signal.
Applications of PM:
- PM is used in analog communication systems, particularly in certain types of analog satellite communication.
- It is also employed in certain types of radar systems.
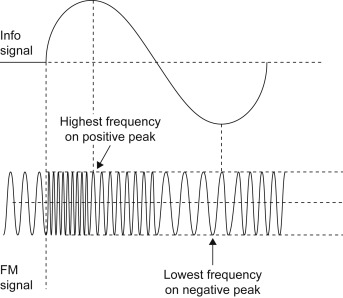
2. Frequency Modulation (FM):
Analysis of FM:
Frequency Deviation (Δf): It represents the maximum frequency change in hertz and is proportional to the peak amplitude of the message signal.
Applications of FM:
- FM is widely used in high-fidelity audio broadcasting.
- It is the standard modulation technique for VHF and UHF radio communication.
- FM is used in analog television sound transmission.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages: Resilient to amplitude variations, less susceptible to noise compared to AM, and provides good audio quality.
Disadvantages: Requires larger bandwidth, complex implementation compared to AM, and less power-efficient.
Understanding Angle Modulation is essential for designing efficient and high-quality communication systems, especially in the realm of analog signal transmission.





No comments:
Post a Comment