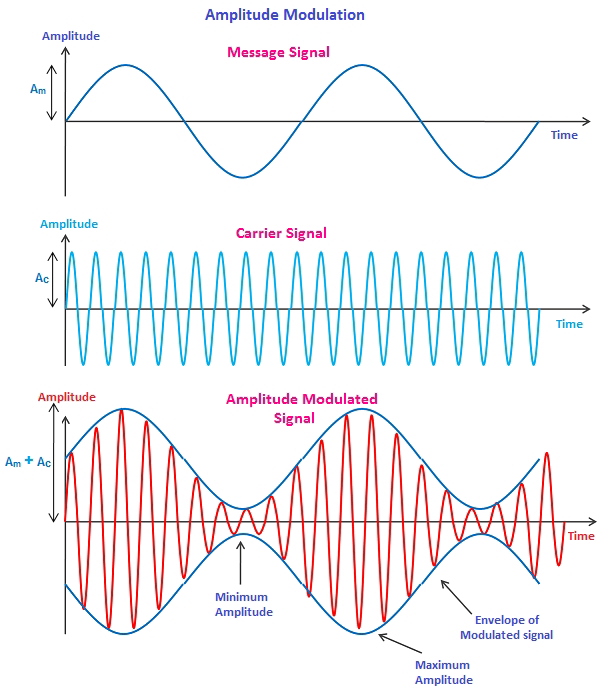
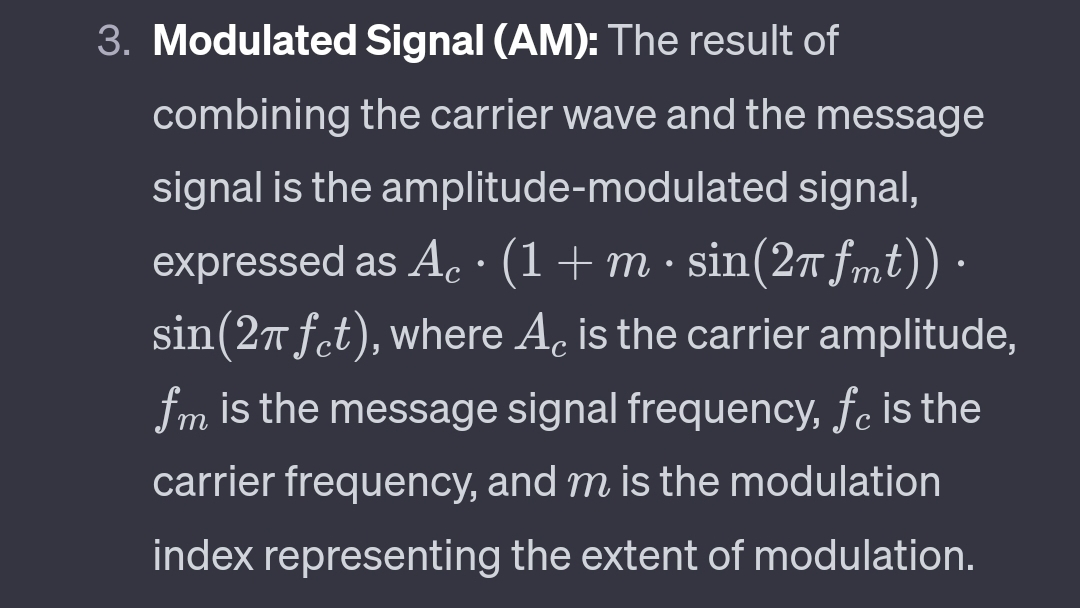
Concept of ASK: Amplitude Shift Keying is a digital modulation technique where the amplitude of a carrier signal is varied to represent different digital states. In ASK, two distinct amplitudes are used to represent binary 0 and 1. The carrier signal is switched between these amplitude levels based on the digital input.
How ASK Works:
Binary Representation: Typically, one amplitude level represents a binary 0, and another represents a binary 1.
Carrier Signal: A high-frequency carrier signal is modulated by changing its amplitude according to the digital input.
Signal Representation: The resulting signal alternates between two amplitude levels, corresponding to the binary sequence.
Benefits of ASK:
Simplicity: ASK is relatively simple to implement, both in terms of modulation at the transmitter and demodulation at the receiver.
Bandwidth Efficiency: ASK can achieve relatively high data rates within limited bandwidth.
Compatibility: ASK can be easily integrated with existing amplitude modulation (AM) systems.
Potential Applications of ASK:
RFID Systems: ASK is commonly used in Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) systems for communication between RFID tags and readers.
Wireless Communication: ASK is suitable for short-range wireless communication systems, such as in remote control devices and certain wireless sensor networks.
Optical Fiber Communication: ASK can be applied in optical fiber communication, where light intensity is modulated to transmit digital information.
Contactless Smart Cards: ASK is employed in contactless smart card technology for secure and efficient data transfer.
Digital Broadcasting: ASK can be used in certain digital broadcasting systems where amplitude variations represent digital information.
Data Transmission in Noisy Environments: ASK can be resilient in noisy environments since it relies on amplitude changes, making it suitable for certain low-cost and power-efficient communication systems.
Considerations:
Susceptibility to Noise: ASK may be more susceptible to noise compared to other digital modulation techniques like Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) or Phase Shift Keying (PSK).
Bandwidth Usage: While ASK can achieve high data rates, it may use more bandwidth compared to more advanced modulation techniques.
In summary, Amplitude Shift Keying is a straightforward digital modulation technique with applications in various communication systems, particularly where simplicity and bandwidth efficiency are important considerations. Its ease of implementation makes it suitable for certain applications, especially in scenarios with lower complexity requirements.