Pulse Modulation is a type of modulation where the amplitude, duration, or position of pulses in a pulse train is varied to convey information. There are several types of pulse modulation, including Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM), Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), and Pulse Position Modulation (PPM).
1. Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM): In PAM, the amplitude of regularly spaced pulses is varied based on the instantaneous amplitude of the message signal. The mathematical representation of a PAM signal is:
Applications of PAM:
- PAM is a fundamental step in the generation of other pulse modulation techniques.
- It is used in some digital communication systems.
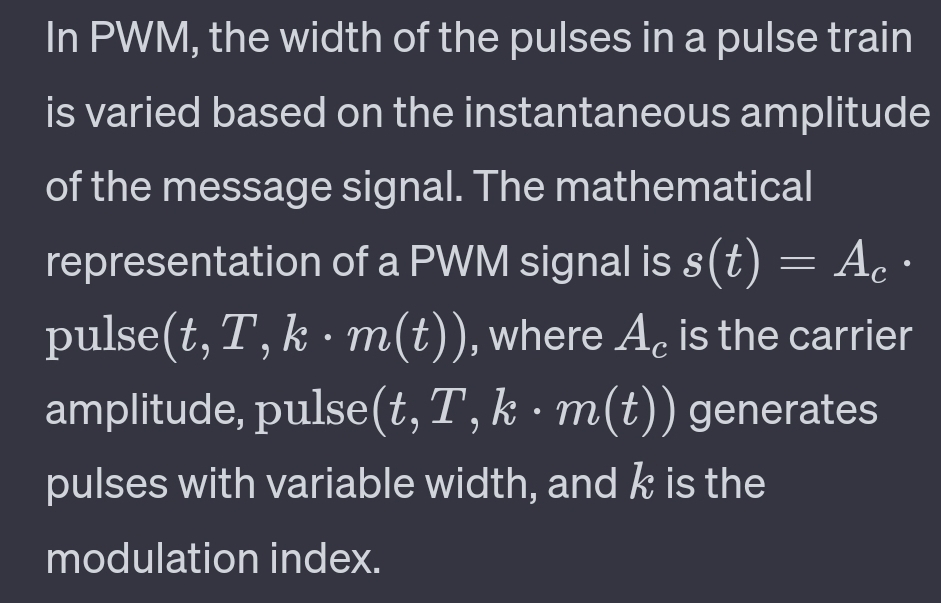
2. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM):
Analysis of PWM:
- Duty Cycle: The ratio of pulse duration to the total time period, representing the percentage of time the pulse is "on."
Applications of PWM:
- PWM is widely used in motor control systems.
- It is utilized in audio amplifiers to generate analog signals from digital sources.
- PWM is employed in power electronics for voltage regulation.
3. Pulse Position Modulation (PPM):
Applications of PPM:
- PPM is used in digital communication systems, especially in optical communication and wireless communication.
- It finds applications in radar systems and data transmission.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pulse Modulation:
Advantages: Efficient use of bandwidth, immunity to noise, and suitability for digital data transmission.
Disadvantages: Higher complexity in modulation and demodulation processes compared to analog modulation techniques.
Understanding pulse modulation principles is crucial in various fields, especially in digital communication and control systems where digital information needs to be transmitted efficiently.




No comments:
Post a Comment